Data Structure Review
Queue
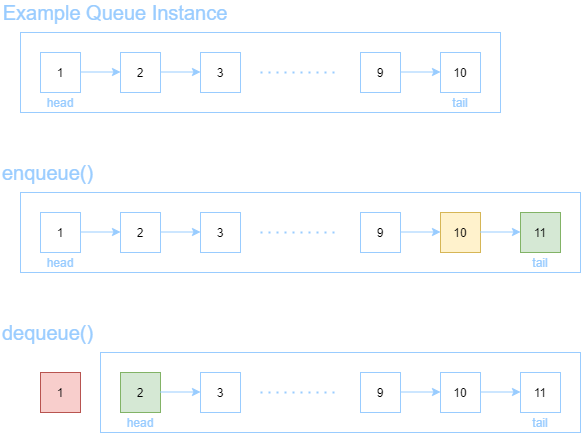
A queue is a first in first out data structure. Elements are served in the order they are inserted. Think of it like a checkout line at your local supermarket; those who line up first in the queue will be served before those that came after.
Queues are typically implemented in terms of linked lists, where the implementation keeps track of both the head and the tail of the list. Pushing to the queue will make a new tail to the linked list while popping from the queue will remove the current head from the linked list.
| Operation | Running Time |
|---|---|
enqueue() |
O(1) |
dequeue() |
O(1) |
Stack
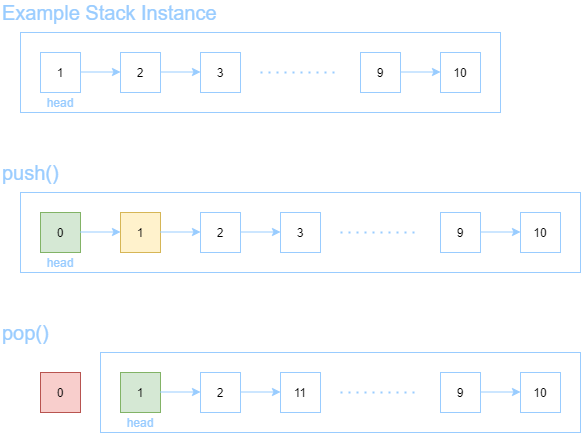
A stack is a first in last out data structure. The latest elements to arrive are served first. Think of it like a pile of heavy textbooks; students return textbooks to the top of the stack while teachers distribute textbooks also from the top of the stack.
Like queues, stacks are also implemented in terms of linked lists, where the implementation keeps track of the head and only the head. Pushing to the stack will make a new head to the linked list while popping from the stack will remove the current head from the linked list.
| Operation | Running Time |
|---|---|
push() |
O(1) |
pop() |
O(1) |
Priority Queue
A priority queue is a data structure where all elements are assigned a comparable weight and then are served in order based on that specific weight.
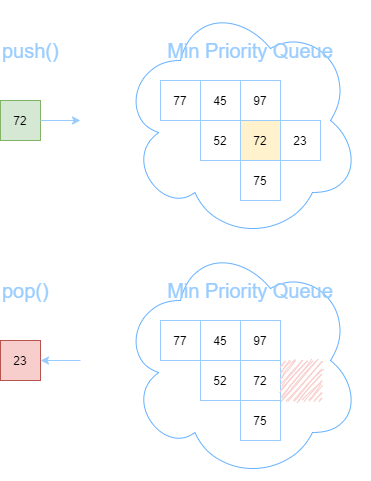
Priority queues can be implemented in many different ways. However, the majority of this unit will involve pushing and popping certain elements in and out of a data structure or decreasing the priority of the same elements. Therefore, we must select an implementation to ensure that such operations are running time efficient.
The table below show an amortized cost analysis of certain data structure operations.
| Data Structure | push() | pop() | decrease() |
|---|---|---|---|
| Linked List | O(n) |
O(1) |
O(n) |
| Heap | O(log n) |
O(log n) |
O(log n) |
| AVL | O(log n) |
O(log n) |
O(log n) |
| Fibonacci Heap | O(1) |
O(log n) |
O(1) |